Loss Functions and Metrics
astroNN provides modified loss functions under astroNN.nn.losses module which are capable to deal with incomplete labels which are represented by magicnumber
in astroNN configuration file or Magic Number in equations below.
Since they are built on Tensorflow and follows Keras API requirement, all astroNN loss functions are fully compatible
with Keras with Tensorflow backend, as well as directly be imported and used with Tensorflow, for most loss functions, the
first argument is ground truth tensor and the second argument is prediction tensor from neural network.
Note
Always make sure when you are normalizing your data, keep the magic number as magic number. If you use astroNN normalizer, astroNN will take care of that.
Here are some explanations on variables in the following loss functions:
\(y_i\) means the ground truth labels, always represented by python variable y_true in astroNN
\(\hat{y_i}\) means the prediction from neural network, always represented by python variable y_pred in astroNN
Correction Term for Magic Number
- astroNN.nn.losses.magic_correction_term(y_true)[source]
Calculate a correction term to prevent the loss being “lowered” by magic_num or NaN
- Parameters
y_true (tf.Tensor) – Ground Truth
- Returns
Correction Term
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
- 2018-Jan-30 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)2018-Feb-17 - Updated - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
Since astroNN deals with magic number by assuming the prediction from neural network for those ground truth with Magic Number is right, so we need a correction term.
The correction term in astroNN is defined by the following equation and we call the equation \(\mathcal{F}_{correction}\)
In case of no labels with Magic Number is presented, \(\mathcal{F}_{correction}\) will equal to 1
Mean Squared Error
- astroNN.nn.losses.mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None)[source]
Calculate mean square error losses
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
Mean Squared Error
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2017-Nov-16 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
MSE is based on the equation
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's loss function first
7model.compile(loss=mean_squared_error, ...)
Mean Absolute Error
- astroNN.nn.losses.mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None)[source]
Calculate mean absolute error, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
Mean Absolute Error
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Jan-14 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
MAE is based on the equation
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's loss function first
7model.compile(loss=mean_absolute_error, ...)
Mean Error
- astroNN.nn.losses.mean_error(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None)[source]
Calculate mean error as a way to get the bias in prediction, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
Mean Error
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-May-22 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
Mean Error is a metrics to evaluate the bias of prediction and is based on the equation
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's loss function first
7model.compile(loss=mean_error, ...)
Regression Loss and Predictive Variance Loss for Bayesian Neural Net
- astroNN.nn.losses.robust_mse(y_true, y_pred, variance, labels_err, sample_weight=None)[source]
Calculate predictive variance, and takes account of labels error in Bayesian Neural Network
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
variance (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Log Predictive Variance
labels_err (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Known labels error, give zeros if unknown/unavailable
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
Robust Mean Squared Error, can be used directly with Tensorflow
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-April-07 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
- astroNN.nn.losses.mse_lin_wrapper(var, labels_err)[source]
Calculate predictive variance, and takes account of labels error in Bayesian Neural Network
- Parameters
var (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Predictive Variance
labels_err (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Known labels error, give zeros if unknown/unavailable
- Returns
Robust MSE function for labels prediction neurones, which matches Keras losses API
- Return type
function
- Returned Funtion Parameter
- function(y_true, y_pred)- y_true (tf.Tensor): Ground Truth- y_pred (tf.Tensor): PredictionReturn (tf.Tensor): Robust Mean Squared Error
- History
2017-Nov-16 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
- astroNN.nn.losses.mse_var_wrapper(lin, labels_err)[source]
Calculate predictive variance, and takes account of labels error in Bayesian Neural Network
- Parameters
lin (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
labels_err (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Known labels error, give zeros if unknown/unavailable
- Returns
Robust MSE function for predictive variance neurones which matches Keras losses API
- Return type
function
- Returned Funtion Parameter
- function(y_true, y_pred)- y_true (tf.Tensor): Ground Truth- y_pred (tf.Tensor): Predictive VarianceReturn (tf.Tensor): Robust Mean Squared Error
- History
2017-Nov-16 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
It is based on the equation implemented as robust_mse(), please notice \(s_i\) is representing \(log((\sigma_{predictive, i})^2 + (\sigma_{known, i})^2)\). Neural network not predicting variance directly to avoid numerical instability but predicting \(log((\sigma_{i})^2)\)
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
They basically do the same things and can be used with Keras, you just have to import the functions from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3
4 # model for the training process
5 model = Model(inputs=[input_tensor, labels_err_tensor], outputs=[output, variance_output])
6
7 # model for the prediction
8 model_prediction = Model(inputs=input_tensor, outputs=[output, variance_output])
9
10 variance_output = Dense(name='variance_output', ...)
11 output = Dense(name='output', ...)
12
13 predictive_variance_loss = mse_var_wrapper(output, labels_err_tensor)
14 output_loss = mse_lin_wrapper(predictive_variance, labels_err_tensor)
15
16 return model, model_prediction, output_loss, predictive_variance_loss
17
18model, model_prediction, output_loss, predictive_variance_loss = keras_model()
19# remember to import astroNN loss function first
20model.compile(loss={'output': output_loss, 'variance_output': predictive_variance_loss}, ...)
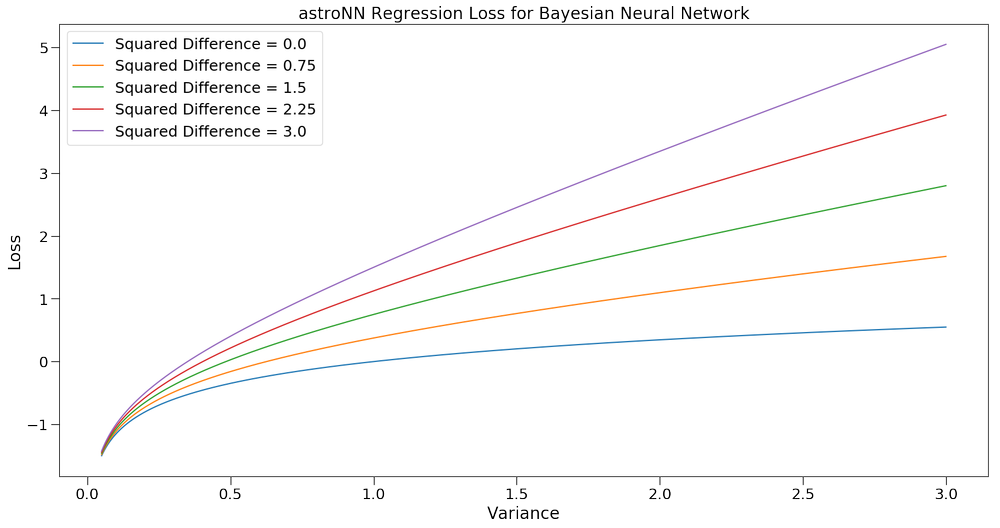
To better understand this loss function, you can see the following plot of Loss vs Variance colored by squared difference which is \((\hat{y_i}-y_i)^2\)
Mean Squared Logarithmic Error
- astroNN.nn.losses.mean_squared_logarithmic_error(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None)[source]
Calculate mean squared logarithmic error, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
Mean Squared Logarithmic Error
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Feb-17 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
MSLE will first clip the values of prediction from neural net for the sake of numerical stability,
Then MSLE is based on the equation
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's loss function first
7model.compile(loss=mean_squared_logarithmic_error, ...)
Mean Absolute Percentage Error
- astroNN.nn.losses.mean_absolute_percentage_error(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None)[source]
Calculate mean absolute percentage error, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
Mean Absolute Percentage Error
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Feb-17 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
Mean Absolute Percentage Error will first clip the values of prediction from neural net for the sake of numerical stability,
Then Mean Absolute Percentage Error is based on the equation
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's loss function first
7model.compile(loss=mean_absolute_percentage_error, ...)
Mean Percentage Error
- astroNN.nn.losses.mean_percentage_error(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None)[source]
Calculate mean percentage error, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
Mean Percentage Error
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Jun-06 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
Mean Percentage Error will first clip the values of prediction from neural net for the sake of numerical stability,
Then Mean Percentage Error is based on the equation
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's loss function first
7model.compile(loss=mean_percentage_error, ...)
Categorical Cross-Entropy
- astroNN.nn.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None, from_logits=False)[source]
Categorical cross-entropy between an output tensor and a target tensor, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
from_logits (boolean) – From logits space or not. If you want to use logits, please use from_logits=True
- Returns
Categorical Cross-Entropy
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Jan-14 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
Categorical Cross-Entropy will first clip the values of prediction from neural net for the sake of numerical stability if the prediction is not coming from logits (before softmax activated)
and then based on the equation
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's loss function first
7model.compile(loss=categorical_crossentropy(from_logits=False), ...)
Binary Cross-Entropy
- astroNN.nn.losses.binary_crossentropy(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None, from_logits=False)[source]
Binary cross-entropy between an output tensor and a target tensor, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
from_logits (boolean) – From logits space or not. If you want to use logits, please use from_logits=True
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
Binary Cross-Entropy
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Jan-14 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
Binary Cross-Entropy will first clip the values of prediction from neural net for the sake of numerical stability if
from_logits=False
and then based on the equation
to avoid numerical instability if from_logits=True, we can reformulate it as
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's loss function first
7model.compile(loss=binary_crossentropy(from_logits=False), ...)
Categorical Cross-Entropy and Predictive Logits Variance for Bayesian Neural Net
- astroNN.nn.losses.robust_categorical_crossentropy(y_true, y_pred, logit_var, sample_weight)[source]
Calculate categorical accuracy, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction in logits space
logit_var (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Predictive variance in logits space
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
categorical cross-entropy
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Mar-15 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
- astroNN.nn.losses.bayesian_categorical_crossentropy_wrapper(logit_var)[source]
- Categorical crossentropy between an output tensor and a target tensor for Bayesian Neural Networkequation (12) of arxiv:1703.04977
- Parameters
logit_var (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Predictive variance
- Returns
Robust categorical_crossentropy function for predictive variance neurones which matches Keras losses API
- Return type
function
- Returned Function Parameter
- function(y_true, y_pred)- y_true (tf.Tensor): Ground Truth- y_pred (tf.Tensor): Prediction in logits spaceReturn (tf.Tensor): Robust categorical crossentropy
- History
2018-Mar-15 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
- astroNN.nn.losses.bayesian_categorical_crossentropy_var_wrapper(logits)[source]
- Categorical crossentropy between an output tensor and a target tensor for Bayesian Neural Networkequation (12) of arxiv:1703.04977
- Parameters
logits (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction in logits space
- Returns
Robust categorical_crossentropy function for predictive variance neurones which matches Keras losses API
- Return type
function
- Returned Function Parameter
- function(y_true, y_pred)- y_true (tf.Tensor): Ground Truth- y_pred (tf.Tensor): Predictive variance in logits spaceReturn (tf.Tensor): Robust categorical crossentropy
- History
2018-Mar-15 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
It is based on Equation 12 from arxiv:1703.04977. \(s_i\) is representing the predictive variance of logits
where Distorted Categorical Cross-Entropy is defined as
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
bayesian_categorical_crossentropy_wrapper is for the prediction neurones
bayesian_categorical_crossentropy_var_wrapper is for the predictive variance neurones
They basically do the same things and can be used with Keras, you just have to import the functions from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3
4 # model for the training process
5 model = Model(inputs=[input_tensor], outputs=[output, variance_output])
6
7 # model for the prediction
8 model_prediction = Model(inputs=input_tensor, outputs=[output, variance_output])
9
10 variance_output = Dense(name='predictive_variance', ...)
11 output = Dense(name='output', ...)
12
13 predictive_variance_loss = bayesian_categorical_crossentropy_var_wrapper(output)
14 output_loss = bayesian_categorical_crossentropy_wrapper(predictive_variance)
15
16 return model, model_prediction, output_loss, predictive_variance_loss
17
18model, model_prediction, output_loss, predictive_variance_loss = keras_model()
19# remember to import astroNN loss function first
20model.compile(loss={'output': output_loss, 'variance_output': predictive_variance_loss}, ...)
Binary Cross-Entropy and Predictive Logits Variance for Bayesian Neural Net
- astroNN.nn.losses.robust_binary_crossentropy(y_true, y_pred, logit_var, sample_weight)[source]
Calculate binary accuracy, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction in logits space
logit_var (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Predictive variance in logits space
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
categorical cross-entropy
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Mar-15 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
- astroNN.nn.losses.bayesian_binary_crossentropy_wrapper(logit_var)[source]
- Binary crossentropy between an output tensor and a target tensor for Bayesian Neural Networkequation (12) of arxiv:1703.04977
- Parameters
logit_var (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Predictive variance
- Returns
Robust binary_crossentropy function for predictive variance neurones which matches Keras losses API
- Return type
function
- Returned Function Parameter
- function(y_true, y_pred)- y_true (tf.Tensor): Ground Truth- y_pred (tf.Tensor): Prediction in logits spaceReturn (tf.Tensor): Robust binary crossentropy
- History
2018-Mar-15 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
- astroNN.nn.losses.bayesian_binary_crossentropy_var_wrapper(logits)[source]
- Binary crossentropy between an output tensor and a target tensor for Bayesian Neural Networkequation (12) of arxiv:1703.04977
- Parameters
logits (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction in logits space
- Returns
Robust binary_crossentropy function for predictive variance neurones which matches Keras losses API
- Return type
function
- Returned Function Parameter
- function(y_true, y_pred)- y_true (tf.Tensor): Ground Truth- y_pred (tf.Tensor): Predictive variance in logits spaceReturn (tf.Tensor): Robust binary crossentropy
- History
2018-Mar-15 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
It is based on Equation 12 from arxiv:1703.04977. \(s_i\) is representing the predictive variance of logits
where Distorted Binary Cross-Entropy is defined as
And thus the loss for mini-batch is
bayesian_binary_crossentropy_wrapper is for the prediction neurones
bayesian_binary_crossentropy_var_wrapper is for the predictive variance neurones
They basically do the same things and can be used with Keras, you just have to import the functions from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3
4 # model for the training process
5 model = Model(inputs=[input_tensor], outputs=[output, variance_output])
6
7 # model for the prediction
8 model_prediction = Model(inputs=input_tensor, outputs=[output, variance_output])
9
10 variance_output = Dense(name='predictive_variance', ...)
11 output = Dense(name='output', ...)
12
13 predictive_variance_loss = bayesian_binary_crossentropy_var_wrapper(output)
14 output_loss = bayesian_binary_crossentropy_wrapper(predictive_variance)
15
16 return model, model_prediction, output_loss, predictive_variance_loss
17
18model, model_prediction, output_loss, predictive_variance_loss = keras_model()
19# remember to import astroNN loss function first
20model.compile(loss={'output': output_loss, 'variance_output': predictive_variance_loss}, ...)
Categorical Classification Accuracy
- astroNN.nn.losses.categorical_accuracy(y_true, y_pred)[source]
Calculate categorical accuracy, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
- Returns
Categorical Classification Accuracy
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Jan-21 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
Categorical Classification Accuracy will first deal with Magic Number
Then based on the equation
And thus the accuracy for is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's metrics function first
7model.compile(metrics=categorical_accuracy, ...)
Note
Please make sure you use categorical_accuracy when using categorical_crossentropy as the loss function
Binary Classification Accuracy
- astroNN.nn.losses.binary_accuracy(*args, **kwargs)[source]
Calculate binary accuracy, ignoring the magic number
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
- Returns
Binary accuracy
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-Jan-31 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
Binary Classification Accuracy will round the values of prediction if from_logits=False or will apply sigmoid
first and then round the values of prediction if from_logits=True
and then based on the equation
And thus the accuracy for is
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's metrics function first
7model.compile(metrics=binary_accuracy(from_logits=False), ...)
Note
Please make sure you use binary_accuracy when using binary_crossentropy as the loss function
Zeros Loss
- astroNN.nn.losses.zeros_loss(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None)[source]
Always return zeros
- Parameters
y_true (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Ground Truth
y_pred (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable)) – Prediction
sample_weight (Union(tf.Tensor, tf.Variable, list)) – Sample weights
- Returns
Zeros
- Return type
tf.Tensor
- History
2018-May-24 - Written - Henry Leung (University of Toronto)
zeros_loss is a loss function that will always return zero loss and the function matches Keras API. It is mainly
designed to do testing or experiments.
It can be used with Keras, you just have to import the function from astroNN
1def keras_model():
2 # Your keras_model define here
3 return model
4
5model = keras_model()
6# remember to import astroNN's loss function first
7model.compile(loss=zeros_loss, ...)